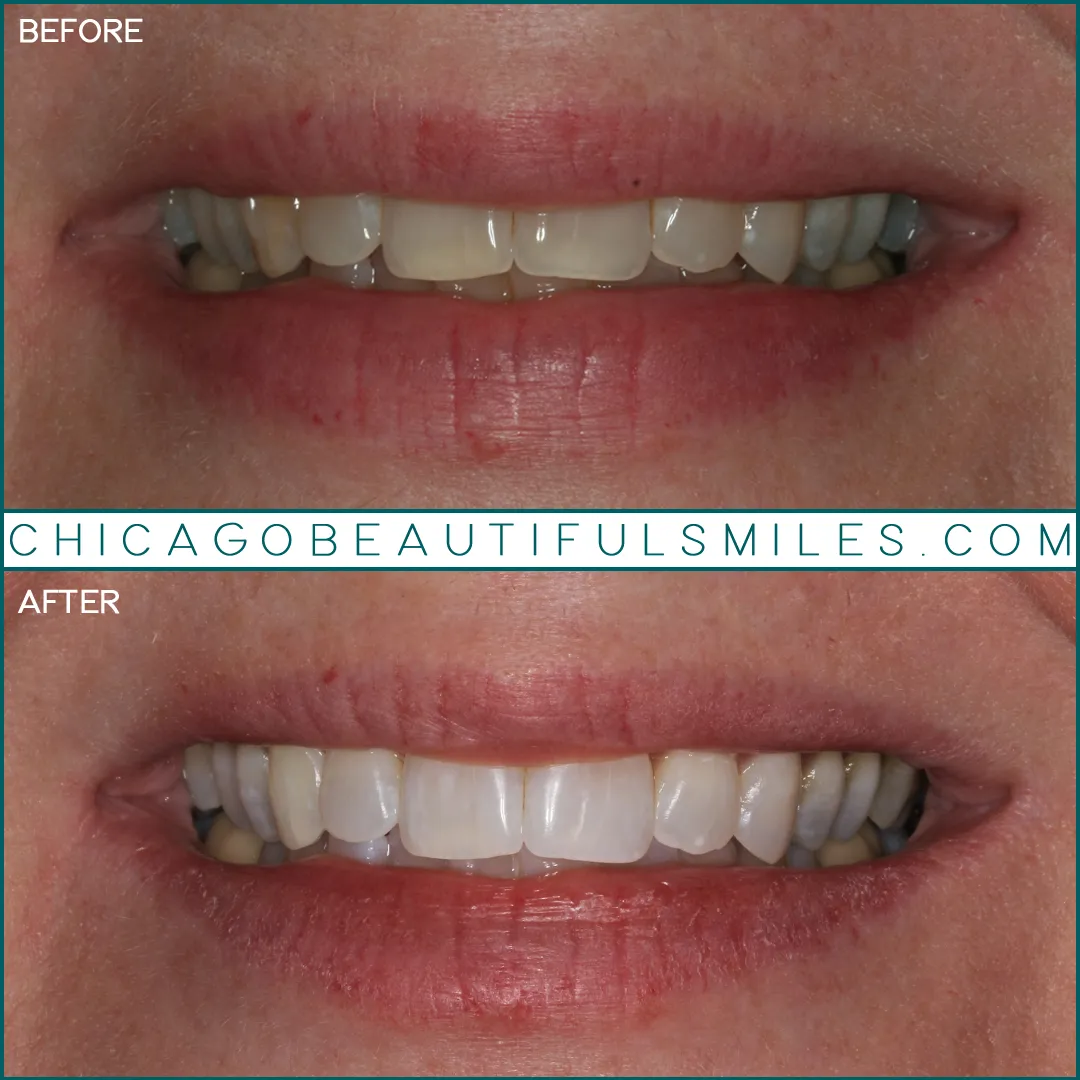
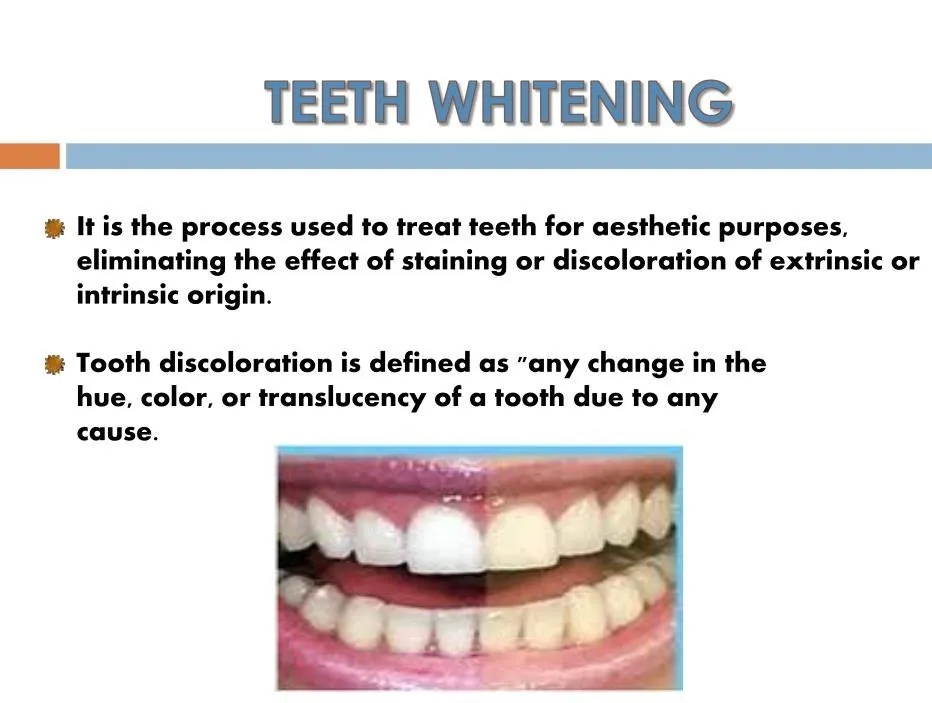
The Science of Teeth Whitening
Teeth whitening is more than just a cosmetic procedure; it’s a fascinating chemical process. Understanding the science behind it allows you to make informed decisions about your oral health. The goal is to remove stains and discoloration from the teeth, revealing a brighter, more confident smile. This process primarily targets the enamel and dentin, the outer and inner layers of your teeth. This is a delicate process, so understanding how it works ensures you get the best results.
The Chemistry of Discoloration
Tooth discoloration occurs when stains penetrate the porous enamel or accumulate on the tooth’s surface. These stains can be caused by a variety of factors, including the foods and drinks we consume, lifestyle choices, and even aging. Over time, these stains can lead to a dull or yellowed appearance, which many people find undesirable. The process is accelerated by the constant exposure of teeth to external elements. Therefore, the chemistry of discoloration is fundamental to understanding how whitening treatments work.
Understanding Enamel and Dentin

Enamel, the outermost layer of the tooth, is the hardest substance in the human body. It’s also porous, which means it can absorb stains over time. Beneath the enamel lies dentin, a softer, yellowish tissue. The color of your teeth is largely determined by the dentin, which can become more visible as the enamel thins or is stained. Therefore, teeth whitening aims to address stains on both the enamel’s surface and the underlying dentin to achieve the desired results. The varying porosity of the enamel and dentin affects the speed and effectiveness of whitening treatments.
Common Causes of Tooth Discoloration
Numerous factors contribute to tooth discoloration. Dietary habits play a significant role; coffee, tea, red wine, and dark-colored berries are notorious stainers. Smoking and other tobacco products also lead to significant discoloration due to the presence of nicotine and tar. Additionally, aging causes enamel to thin, making the underlying dentin more visible. Certain medications, such as tetracycline, can cause internal tooth discoloration, and poor oral hygiene exacerbates the problem. The accumulation of plaque and tartar further contributes to the problem. The combined effect of these factors influences the need for teeth whitening.
How Whitening Agents Work
Teeth whitening agents use chemical reactions to break down the stain molecules within the enamel and dentin. These agents penetrate the tooth’s surface and react with the discolored compounds, effectively breaking them apart. This process doesn’t actually remove the enamel but rather alters the stain molecules so that they reflect less light and appear lighter. The effectiveness of whitening agents depends on the concentration of the active ingredients and the duration of the treatment. Different agents are used in professional and at-home treatments, each designed to address the needs of the user.
Hydrogen Peroxide’s Role
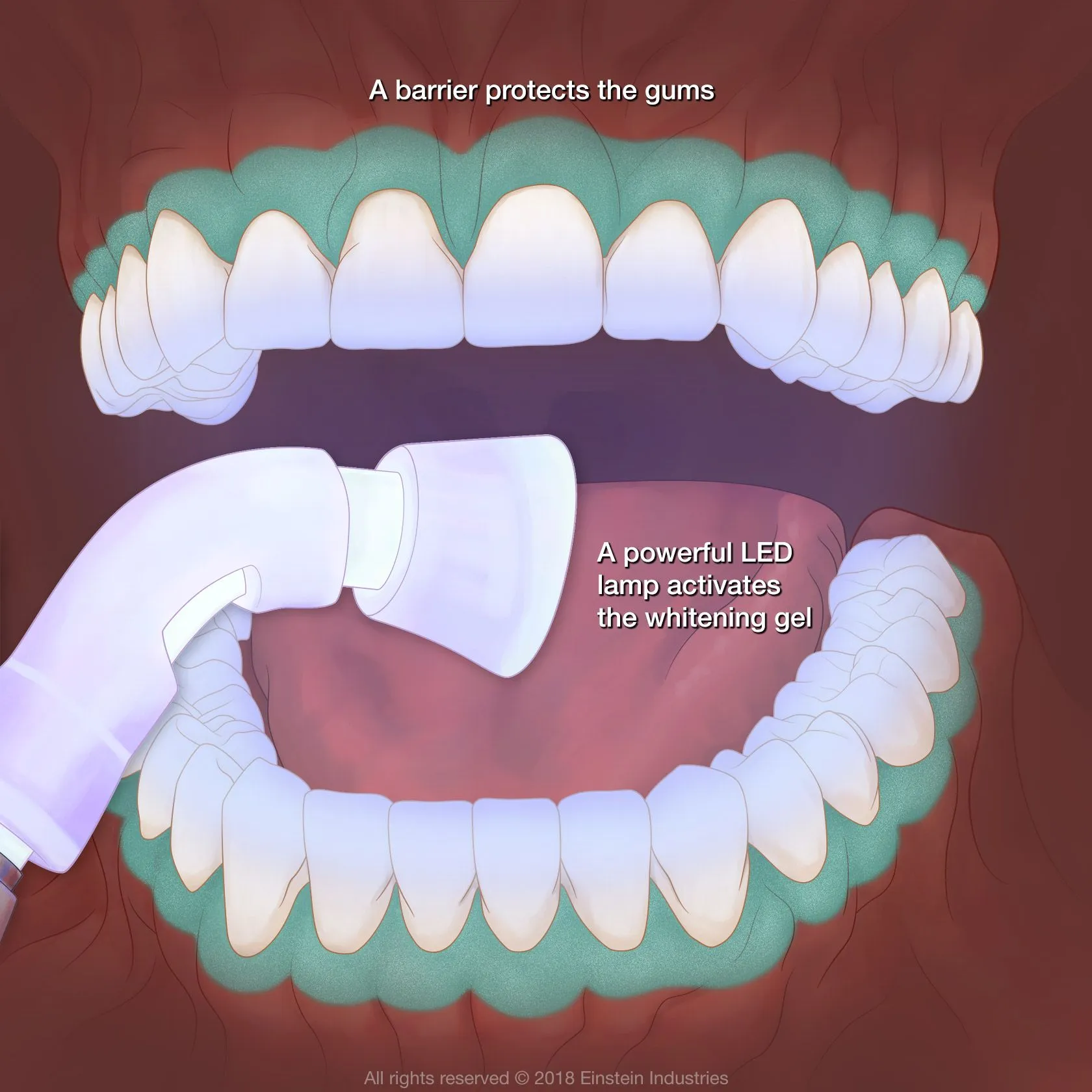
Hydrogen peroxide is a primary active ingredient in many teeth whitening products. It is a strong oxidizing agent, meaning it readily donates oxygen molecules. When hydrogen peroxide comes into contact with the stained tooth structure, it releases these oxygen molecules. These oxygen molecules react with the stain molecules, breaking them down into smaller, less visible components. The effectiveness of hydrogen peroxide depends on its concentration; higher concentrations are used in professional treatments, offering faster results. The process allows the whitening agent to go deep into the tooth and break down difficult stains.
Carbamide Peroxide’s Function
Carbamide peroxide is another common whitening agent, often found in at-home treatments. It breaks down into hydrogen peroxide and urea when it comes into contact with water. The hydrogen peroxide then performs the same stain-removing action as described above, but the urea acts as a buffering agent. It helps to control the release of hydrogen peroxide and reduces the potential for tooth sensitivity. This slower release makes carbamide peroxide suitable for longer-duration treatments such as overnight trays. This process is also beneficial for achieving effective teeth whitening.
The Chemical Reaction Explained
The chemical reaction in teeth whitening involves oxidation. The active whitening agents, hydrogen peroxide or those derived from carbamide peroxide, release oxygen free radicals. These unstable oxygen molecules react with the stain molecules. This reaction effectively breaks the bonds that hold the stain molecules together, changing their structure. As a result, the larger, complex stain molecules are broken down into smaller, less noticeable components. This process changes how light reflects off the tooth’s surface, making it appear whiter. This is how a bright smile is achieved.
The Role of Oxygen

Oxygen plays a crucial role in the teeth whitening process. The oxygen molecules released by the whitening agents are highly reactive. They act as the main force behind breaking down the stain molecules. The oxygen radicals generated during the oxidation reaction work on a molecular level. They disrupt the chromophores, the parts of the stain molecules that absorb light and give them their color. By breaking down these chromophores, the overall appearance of the teeth becomes lighter and brighter. The oxygen molecules are, therefore, the key players.
Types of Teeth Whitening
Several methods are available for teeth whitening, each with its own approach and level of effectiveness. These range from professional treatments performed by dentists to various at-home options. Choosing the right method depends on individual needs, the severity of the staining, and desired results. The process will vary in terms of cost, convenience, and the amount of time invested. Understanding the different types helps you choose what suits you.
Professional Whitening Treatments
Professional teeth whitening, conducted by a dentist, typically involves the use of high-concentration hydrogen peroxide gels. These treatments are applied directly to the teeth, often combined with a special light or laser to accelerate the chemical reaction. The process is closely monitored to ensure safety and effectiveness, and results are often seen in a single visit. Dentists can address more severe staining cases. The ability of professionals to ensure proper isolation of the teeth and gums minimizes the risk of side effects, ensuring a safe and effective whitening experience. The benefits of professional treatments are readily noticeable.
At-Home Whitening Options
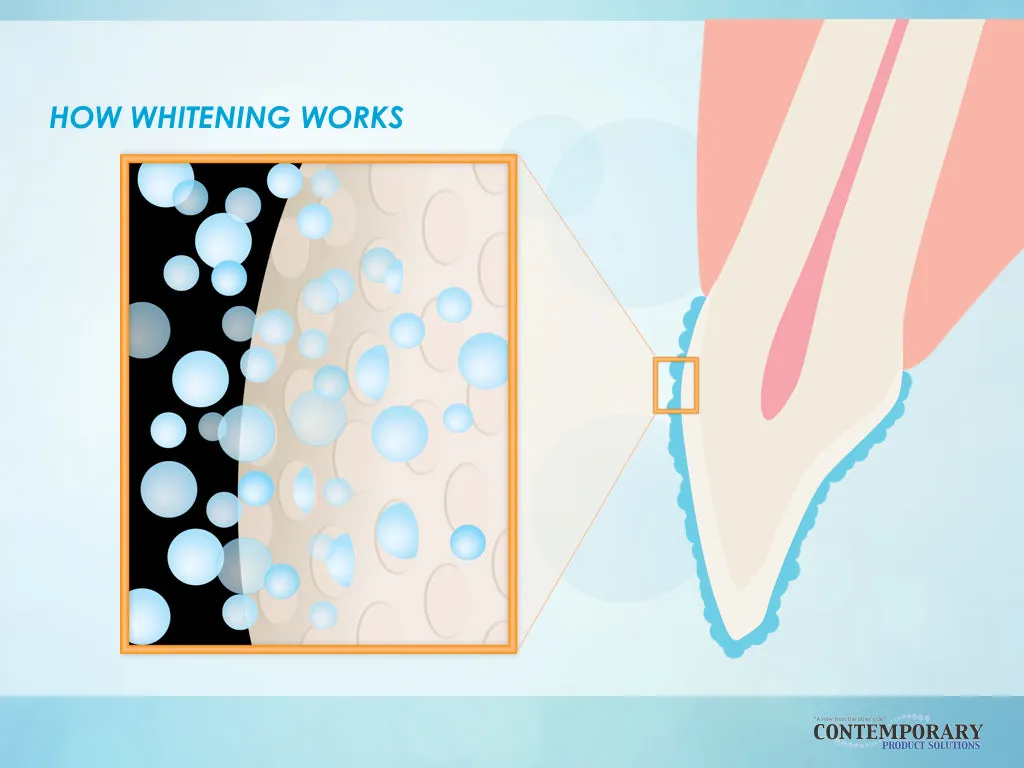
At-home whitening options provide more flexibility and are often more affordable. These include whitening strips, custom-fitted trays with whitening gel, and over-the-counter whitening kits. The effectiveness of these options varies depending on the concentration of the active ingredients and the frequency of use. Although at-home treatments may require more time to achieve desired results, they can still be very effective. It is essential to follow the instructions carefully to avoid potential side effects, such as tooth sensitivity. These methods can also be combined with professional treatments for optimal results.
Whitening Toothpastes
Whitening toothpastes are a common and accessible option for maintaining a brighter smile. They often contain mild abrasives or chemical agents that help remove surface stains. While whitening toothpastes can improve the appearance of your teeth, they typically do not provide the same level of whitening as professional treatments or more concentrated at-home products. Using them consistently can help prevent new stains from forming and maintain a brighter appearance. When choosing a whitening toothpaste, look for products that are gentle on the enamel to avoid abrasion.
Effectiveness and Safety
The effectiveness of teeth whitening depends on several factors, including the type of treatment, the severity of the staining, and individual tooth characteristics. While teeth whitening is generally safe, some potential side effects should be considered. Understanding both the benefits and risks allows you to make informed decisions and take steps to minimize any negative impacts. You must be mindful of the processes involved, which helps in effective and safe outcomes.
Potential Side Effects
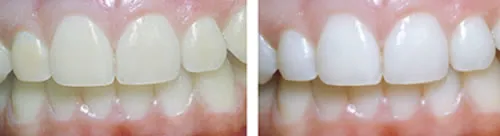
The most common side effects of teeth whitening include tooth sensitivity and gum irritation. Sensitivity often occurs because the whitening agents can penetrate the enamel and reach the nerves in the teeth. Gum irritation can result from the whitening agent coming into contact with the soft tissues of the mouth. These side effects are usually temporary and subside shortly after the treatment is completed. More serious side effects are rare but can include damage to the tooth enamel if the treatment is misused or overused. Using the products correctly can minimize these issues.
How to Minimize Sensitivity
Several strategies can minimize tooth sensitivity during and after teeth whitening. Using a toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth can help block the tubules in the dentin. Avoiding extremely hot or cold foods and drinks can also reduce sensitivity. A dentist can provide fluoride treatments or prescribe desensitizing agents to use before and after whitening treatments. Following the instructions carefully and not over-whitening your teeth is crucial. These steps contribute to a more comfortable whitening experience.
Long-Term Results and Maintenance
Teeth whitening results are not permanent, and maintaining a bright smile requires ongoing care and maintenance. This involves following a proper oral hygiene routine, making dietary adjustments, and considering touch-up treatments when necessary. Understanding the factors influencing the longevity of the results helps you enjoy a brighter smile for a longer period. This long-term view also impacts oral health positively.
Dietary Considerations
Certain foods and drinks can stain teeth and diminish the effects of whitening treatments. To maintain your results, limit your consumption of coffee, tea, red wine, and dark-colored berries. Foods with strong colors, like curries and soy sauce, should also be consumed in moderation. Rinsing your mouth with water after eating or drinking staining substances can help. You can also use a straw to minimize contact with your teeth. Being mindful of your diet helps prevent new stains and prolong the results of teeth whitening.
Maintaining a Bright Smile
Maintaining a bright smile involves a combination of regular dental checkups, proper oral hygiene, and, if needed, touch-up whitening treatments. Brushing and flossing regularly remove surface stains and prevent plaque buildup. Using a whitening toothpaste can also help maintain brightness. Consider professional touch-up treatments from your dentist to maintain the best results. Maintaining a bright smile improves your confidence and boosts overall oral health. Regular maintenance guarantees a long-lasting, bright smile.